Research Article - (2025) Volume 8, Issue 1
How the Electrons Moves Through Tunnel Transition According to New Axioms and Laws
Received Date: Jan 14, 2025 / Accepted Date: Feb 24, 2025 / Published Date: Mar 07, 2025
Copyright: ©├?┬ę2025 Dr. Valentina Markova. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Citation: Markova, V. (2025). How the Electrons Moves Through Tunnel Transition According to New Axioms and Laws. Adv Theo Comp Phy, 8(1), 01-08.
Abstract
The Theory of new Axioms and Laws contains 2 new Axioms and 8 new Laws and is created by the same author. It claims that electron is constructed simultaneously from 2 different vortices: open decelerating transverse vortex and open accelerating longitudinal vortex (Axiom1). They are mutual orthogonal in space (perpendicular in S) and pulsate in time (antiphase in T). Pulsating in time (T) the transverse vortex forms the Real time-space (of light and Electromagnetic waves). Pulsating in time (T) the longitudinal vortices have ability to pack, through they inserte each other and form an longitudinal Funnel. The longitudinal Funnels generate an unique time-space of Gravitational field.
The electron is generated by a transverse decelerating vortex. It is coiled transversely from out to inward and forms the electron"s body like an toroid with radius (r). In center of toroid is generated a longitudinal accelerating Funnel with length (l) perpendicular to plane of toroid (Law1). The electron changes the ratio between its parameters (r and l) depending on the phase of its pulsation in time (T).
In first phase of pulsation in time (T) the electron inflates to an expanded toroid has a maximum radius (r) of the transverse vortex of toroid body and a minimum length (l) of the longitudinal vortex:(r>l). The electron becomes clearly visible to an outside observer and is perceived as particle.
In second phase of the pulsation, the electron contracts to a “point” with a minimum radius (r) and the longitudinal vortex stretches to a maximum length (l): (l>r). Thus electron has an almost zero mass, it becomes invisible to an outside observer and is perceived as wave.
When an electron hits in a potential barrier, according new Theory of new Axioms and Laws, it as transverse vortex (particle for the T/2 period) cannot pass through the potential barrier. Thus electron as a particle (l
Only the longitudinal vortex (as wave for the next T/2 period) can pass through the potential barrier. Thus the electron as a wave (l>r) can be both on this side, and on that side of the barrier- the place is probabilistic.
Therefore the Theory of new Axioms and Laws specifies that the quantum superposition is a real only for the wave part (as longitudinal vortex) of electron for half of period (T/2) of pulsation.
And it follows an assumption : all free electrons randomly distributed in space (S) emit in random phases in time for half of the pulsation period (T/2) their longitudinal accelerating vortices and create a probabilistically distributed field with quantum superposition.
Introduction
Essence of the Problem
The modern understanding of Quantum Mechanics regarding the possibility of an electron crossing a potential barrier using tunnel transition is described in a condensed form on Wikipedia.
Wikipedia: “Tunnel transition or Tunnel effect is the quantum mechanical effect of passing through a classically forbidden energy state (energy barrier)".
“The tunnel effect is the passage of electrons through a potential barrier, the height of which is greater than the electron's own energy. Such a passage is possible when the width of the transition is small enough, commensurate with the interatomic distances".
“In this way, they overcome the barrier as if through a tunnel, despite the fact that their energy is less than the height of the potential barrier. (When overcoming the barrier, the electrons do not pass through it - due to the uncertainty of their location due to their wave nature, the electrons have the probability of being at a point on the other side of the potential barrier)”
According Theory of new Axioms and Laws
According the Axiom of Classical Field Theory: div (rot E)=0 [1].
According new Axiom1: A field in which the vector E moves with a monotonically non-uniform speed (Decelerating or accelerating) becomes an open vortex field structure: div (rot E) is not equal to zero (0) [2,3,4].
The Axiom 1 claims that there are 2 type open vortices - transverse (in plane 2D) (Figure 1,a,1) and longitudinal (in volume 3D ) (Figure 1,a,2). Each of them can be accelerating or decelerating. Therefore we receive 4 type of open vortices.
According Axiom2: There are mutually orthogonal field structures that form a resonant system by exchanging energy and matter with each other, (Figure1,a,b) [2,3,4].
Axiom2 claims that orthogonal pairs form 6 pairs of particles (connected in the right direction) and 6 pairs of antiparticles (connected in the opposite direction) (Not pictures). The main pair of particles is electron – proton (Figure1,a,b). Their generating direction is from proton to electron. There are pair and inverse direction that form positron and antiproton.
According Law1: A decelerating transverse vortex in plane 2D generates in its center perpendicular in volume 3 D accelerating longitudinal vortex (Figure 1,a: electron) [3,4].
According Law2: A decelerating longitudinal vortex in volume 3D generates in center of perpendicular plane in 2D an accelerating transverse vortex (Figure 1,b: proton) [4,5].
Law 6 for 2D: The main accelerating vortex (in 2D) has increasing longitudinal velocity (V) and sucks inward many primary accelerating vortices with decreasing amplitudes (W), where at every i-th step the variable is changed by a degree (i) of the parameter ψ or ( ψ i), where ψ is equal to the Golden proportion (Figure 1,a,2) [5,6].
Law 6 for 3D: The accelerating vortex in 3D is described with a system of 4 equations in which: longitudinal velocity (V) increases in (n) portions (ψn) times, the angular velocity (w), the amplitude (W) and the number (Nn) of cross vortices decrease to zero in (n) portions (ψ n) times, where the roots v , w and ω and n are

Therefore when velocity (V) increases, the amplitude (W) decreases so that at each step (ni) (according to Consequence of Law 4 and the Law of movement Conservation) the product (Vi). (Wi) is a constant. For an accelerating longitudinal vortex, the amplitude (W) decreases only if it is directed from the outside to inside, ie. if the accelerating vortex sucks in cross vortices with decreasing amplitude (W) [4-6].
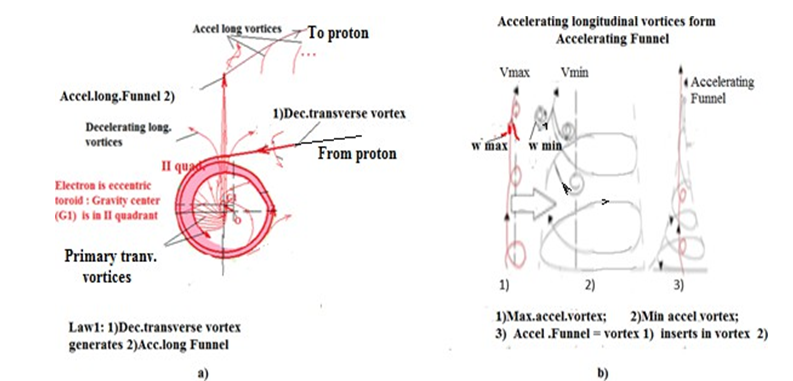
Figure 1: Real Form of Electron
a) The Real Form of Electron, b) The Real Form of Accelerating Funnel
The New Statements According the Theory of New Axioms and Laws
The Theory of new Axioms and Laws describes in detail the structure of the electron. This structure contains 2 mutually orthogonal open vortices (Axiom1): div (rot E) is not equal to zero, where E is the rotating vector. They are mutually orthogonal in space (mutual perpendicular) and in time (pulsating in anti-phase). It is further proven that each of these vortices determines its own type of time- space.
For example: The decelerating transverse vortices (in 2D) are part of a Real time -space, in which we live. The accelerating longitudinal vortices (in 3D) are part of the Gravitational time- space, unknown to us. Therefore, the electron is a complex object that is created by the joint action of 2 types of time-space - Real and Gravitational. So the electron is not just a composite object .It is a complex pulsating structure of 2 different space-times (Real and Gravitational). Given that, one-half of the electron's structure (the Gravitational) is completely unknown to sciences; we cannot guess and predict what its behavior will be.
The Theory of new Axioms and Laws describes this Gravitational part of the electron's structure. Thus it is given much more complete explanation of electron‘s behavior when it passes through a potential barrier. This new Theory describes a new and fuller structure of the electron. Based on the new structure of the electron a few new statements about its behavior are listed here:
1) First Statement: The Electron as a Particle Does Not Pass through Potential Barrier. Only the electron as a wave can pass through the potential barrier. After the barrier, the wave can again collect into a particle. The reason is that the wave can transform itself after barrier.
The transformation means that the longitudinal vortex can reduce its length enough much (to l min) and the number of transverse windings of the transverse vortex automatically increases much enough .Thus the radius of the toroid (r max) increases and it becomes a particle. Alternatively, the sense of transformation is l < r
2) Second Statement: The Electron as Transverse Vortex (Particle, L< R) Is either From This Side or From That Side (A Determinism). But the electron as longitudinal vortex (wave, l
> r) can be both from this side and from that side (an uncertainty).
Proof of First Statement
(Paragraph III, point 1.)”When overcoming the potential barrier, the electron as a particle does not pass through it. Only the electron as a wave passes through the potential barrier. After the barrier, the wave again collects into a particle. This happens as the wave reduces its length (l min) and as a result automatically stretches the radius of the toroid (r max).”
1. Generating of Electron as Toroid by Transverse Vortex
The electron body is generated (according Law1) by the main transverse decelerating vortex in 2D coming from the proton (Figure1a,1). It is winding in the plain 2D and form in Gravitational center of body a perpendicular accelerating vortex in 3D (Figure1a,2).
The more precise this happens in the following way: This main decelerating vortex is wound in the 2D plane and forms a body with a shape similar to a toroid (Figure1a). Since this main transverse vortex is decelerated (according to Law5 for 2D) it emits decelerating primary transverse vortices from itself outwards. In the case of a toroid, the main decelerating vortex emits primary transverse vortices from the periphery to the center of the toroid [3,4].
Generation of Electron as Eccentric
These primary vortices (according Law1) are phased in the Gravitational center (G1) of the toroid in time (T) and space (S). Note: The Gravitational center (G1) does not coincide with the Geometric center (O). It is displaced and is located in the second quadrant of the Cartesian coordinate system. This displacement is a reason the electron to become eccentric. The vector between the Gravitational and Geometric centers (G1-O), called the Eccentricity Vector is projected along the x coordinate (Figure1a) [5,7].
a) Rotation of Electron around Proton
This x-projection determines the repulsion force and the magnitude of the distance to the proton. The Eccentricity Vector is projected along the y coordinate. This y-projection determines the magnitude of the rotation vector around the proton (Not in Figure).
b) Rotation of Electron around Its Axis
The primary decelerating vortices swirl at the point of the location in space (S) of the Gravity Center (G1) (Figure1a). At this point (G1) their transverse velocity becomes zero. The primary decelerating transverse vortices are bended right to left .These primary vortices play role of curved spokes on a wheel. This is the reason all toroid of electron to rotate from right to left [8,11].
Generating of Accelerating Funnel
According Law1 when a transverse vortex is decelerating (regardless of whether it is main or primary vortex) it generates in its center the perpendicular longitudinal acceleration vector. Thus, all primary vortices in the Gravity center (G1) generate the longitudinal acceleration vortices, According Law6 these longitudinal accelerating vortices suck transverse primary vortices from outside to itself. Thus, the most central longitudinal vortices accelerate itself at the expense of more peripheral. Thus, they insert one into another and form a longitudinal accelerating Funnel. In center inserts speediest vortex and outside are winding up more slower and in periphery rolls up the slowest vortex.
Properties of Accelerating Longitudinal Funnel As Gravitational Funnel
Every participant of these accelerating longitudinal vortices does not add up but multiply their speeds.
a) Velocity
If the periphery spiral has minimal velocity (v 0) and the number of spirals in one accelerating Funnel is N (Figure 1b,3) the most central longitudinal vortex can reach a longitudinal velocity ((v0) N).
Result: The longitudinal velocity of central longitudinal vortices of accelerating Funnel can reach size much than light speed.
Thus the longitudinal speed of longitudinal vortices can be greater than the speed of transverse light waves (c): vN =(v )N > c.
b) Complete Resonance
The phasing is to the location (S) and also at time (T). Therefore, in this magic point (G1), a Complete Resonance occurs -resonance at location (S) and in time (T). In real material time - space, there is no such place and such a transformation cannot be performed.
Result: The Complete Resonance exists only in object constructed by mutual orthogonal (in space S and in time T) parts.
Only (according new Theory) in the world of pulsating mutually orthogonal fields transverse and longitudinal vortices can such a transformation be performed.
c) The Real and the Gravity Time-Spaces
Pulsating transverse vortices create transverse waves that propagate transversely with a maximum speed of (c). And each point of the transverse wave moves with a constant speed: T = const. [9].
These pulsating transverse vortices describe the space-time in which humans live. This is also the space-time of light and Electromagnetic waves. Pulsation of longitudinal vortices creates longitudinal waves that propagate longitudinally with a maximum speed: v > c. In the longitudinal Funnel, each longitudinal vortex moves with a different longitudinal speed (v) that forms the height
(H) of spiral. The transverse- angular velocity (w) form radius (R) of toroid .Their ratio is v (H) / w (R). This ratio changes so that the total length (S) of all spirals (Inserted into each other) remains the same: S = const. [11,12].
Result: The Gravitational time-space is done by conservation of ratio v(H )/w (R) so that the total length (S) of all spirals (inserted into each other) remains the same: S = const.
These pulsating longitudinal vortices describe the unique space- time of Gravity ,Gravity forces and Gravitational waves .They propagate longitudinally with a speed (v)N greater than (c) light speed : vN > c .Longitudinal spirals are packaging in Gravitational Funnels and they form spaces between material objects. The decelerating Funnels repel bodies from each other and disperse the body to the less bodies .But the accelerating Funnel attract bodies and form and integrate the bigger body.
d) Gravity Center (G1) is Point of the Transformation from Real to Gravity Time-Space
Inside the electron exists point (G1) where is appeared a unique transformation from Real space-time (T const.) formed by transverse vortices to Gravity space-time (S const.) formed by longitudinal Funnel of inserted longitudinal vortices. Therefore, in Gravitational center (G1) is being done a unique transformation from Real space-time to Gravity space-time.
Result: The Unique Transformation is done in Gravitational Center (G1) From Real Space-Time to Gravity Space-Time.
Therefore electron is generated in border of 2 different time- spaces [5,9,11].
Electron is generated in Border of Real and Gravity Time-Spaces
Electron is a unique particle because it is generated and constructed by 2 mutual orthogonal time spaces: First is a Real time-space by transverse open vortices rolled from outside to the inside in plane (2D) and moving decelerating to the center of electron toroid body.
Second is a Gravitational time-space by accelerating longitudinal vortices in 3D, perpendicular to plane of toroid (2D) that are inserted one into another forming an accelerating Funnel. According the requirement for mutual orthogonal in time (T) (not only in space S) the Real and Gravitational time- space pulsates in time (T) in anti-phases.
For Example: When transverse vortex collapses (r min) then longitudinal vortex becomes longest (l max) or when (l > r) the electron has form of wave. When transverse vortex expands (r max) then longitudinal vortex become shortest (l min) or when (r> l) the electron play role of particle [4,8,10].
Result: Electron is generated in border of Real time-space (T = const.) made by pulsating transverse vortices and Gravity time-spaces (S = const.) made by pulsating longitudinal vortices.
It is not precise to state that the electron is either a particle or a wave the structure of the electron shows that it is both a particle and a wave.
Result: The essence of electron is not either a particle or a wave; the essence of electron is both a particle (as transverse vortices) and wave (as longitudinal vortices).
If we continue to generalize in the world of Classic Mechanics 2 different vectors are summed and a result vector is obtained again; resonant systems include only complementary elements; the equations that describe the phenomena are parametric and are controlled from the outside by selecting parameters and so on.
But the Theory of new Axioms and Laws claims that the result of simultaneous action of 2 mutual orthogonal vectors (longitudinal and transverse speed) they are multiplied and the Total Energy is obtained; resonant systems are formed from mutual orthogonal (in S and in T) elements; the equations are non-parametric (depends only of internal parameter ψn) and cannot be controlled by external parameters [5,6,10].
Result: The result of the simultaneous action of 2 mutually orthogonal vectors is their multiplication and the Total Energy is obtained; the resonant systems are formed from mutual orthogonal elements; the equations are non-parametric and cannot be controlled by external parameters.
Proof of Second Statement
(Paragraph II, point 2) “The electron is either before potential barrier, or after barrier (a determinism). But the wave can be both from this side and from that side (an uncertainty). In the case of the particle (electron), the logic is either-or but in the case of waves and fields, the logic is and-and”.
Electron as transverse vortex (as particle) is located either before, or after barrier: the point is determined
According to Law 1, the electron consists of one part which is transversely coiled with acceleration from outside to inside in a 2D plane in Real space-time. This Real space-time has the characteristics of a material particle. With a larger or smaller radius it always moves transversely and pulsates transversely, emitting concentric transverse waves, the points of which propagate with the same speed: T = const. [7,8].
When there is a potential barrier, the electron in the form of a particle (r > l) can be located either before the barrier or after the barrier, as its location is determined [9].
Result: The transverse vortices cannot pass (determinately) through the potential barrier. Thus, the particle cannot be located in both places at the same time.
Result: The particle can located either before, or after barrier (determined place) The particle is unable to pass through a potential barrier. The reason is that the transverse vortex experiences maximum resistance when passing through the potential barrier. The maximum resistance occurs because the potential barrier is also a material medium that is constructed of transverse vortices. When one transverse vortex meets another transverse vortex, the resistance it experiences is like a head-on collision
Result: The resistance is maximal when the transverse vortex of particle meets the transverse vortex of potential barrier. The reason is that the barrier is constructed also by transverse vortices .Thus the transverse vortex of electron crashes into transverse vortices of barrier. That is why transverse vortex of electron particle cannot pass through the transverse vortices of barrier. Thus, the potential barrier is also a material medium that is constructed of transverse vortices. That is why the particle is located either before the barrier or after the barrier.
Result: The resistance is minimal when the longitudinal vortex of particle passes through the transverse vortex of potential barrier.
The reason is that the longitudinal vortex crosses the space between the filaments of the transverse vortex of the barrier unhindered. It becomes clear that the potential barrier is opaque to the transverse vortex of the electron as a particle for the half-period (T/2). Result: The potential barrier is opaque to the electron particle (as transverse vortex) and transparent to the electron wave (as longitudinal vortices).
The potential barrier is transparent only to the longitudinal vortex of the electron as a wave for the half-period (T/2).
Electron as wave is located both before-and after barrier: the place is probabilistic.
According to Law 1, the electron consists of a second part, which contains longitudinally coiled vortices with positive (+) acceleration from the Gravity center (G1) to up in a 3D volume. They form accelerating Funnel with Gravitational space-time. This second part is Gravitational space-time and has the characteristics of a longitudinal ( not transverse ) vortices .With a greater or lesser length of the longitudinal spiral, this wave always moves longitudinally and pulsates longitudinally, emitting longitudinal vortices. Their spirals are inserted into each other, preserving the same total length: S = const. [8.10,12].
Result: The accelerating longitudinal vortices (and accelerating Funnel) can pass (probably) through the potential barrier.
Only in the form of a wave (l > r) the electron can possibly cross the potential barrier, but it may not pass - it may be reflected.
Result: The accelerating longitudinal vortex can be located both before and after barrier (probabilistic place).
The wave can pass completely, can pass partially but it can reflect or process is probabilistic. The wave can be located in both places - before and after the barrier.
Result: The resistance is minimal when the longitudinal vortex of particle passes through the transverse vortex of potential barrier, because the longitudinal vortex pierces (flows) between threads of the transverse vortices.
That is why the wave can be positioned with some possibility or before, or after barrier.
Proposal
The Quantum superposition does not apply to particles. It is not precise to state that the electron as a particle can be located at any given place in space- both here and there at the same time. The Quantum superposition is true only for only to waves.
According to Quantum Theory, the electron contains both a particle and a wave. But the definition of a particle is unclear and a wave is a transverse closed wave of the light wave type.
According to the Theory of the new Axioms and Laws, the particle contains an open transverse vortex coiled with acceleration in 2D, and the wave is a longitudinal open vortex coiled with acceleration in 3D. Both of these two vortices are mutual orthogonal (in the space S and in time T) each other.
According to the Theory of the new Axioms and Laws, the particle contains an open pulsating transverse vortex coiled with acceleration in 2D, and the wave appears a pulsating longitudinal open vortex coiled with acceleration in 3D .Both of these two vortices are mutual orthogonal (in the space S and in time T) each other.
According Quantum Mechanics the particle consists only a closed vortex coiled without acceleration (evenly wound) in 2D. The second vortex in 3D is absented.
Before we do proposal the following conclusions are necessary to right:
Conclusion: There are differences in the structure of the electron described in Quantum mechanics and in the Theory of the new Axioms and Laws.
Thus at any place in space (S) there can be a free electron that pulsates in time (T). This means that at any random point an electron can live in a collapsed phase (l > r) and emit a longitudinal wave. Therefore, at many random points in space (S) the free electrons can become in a collapsed state for half (T/2) of the pulsation period and emit longitudinal waves, although in different phases (0-180 angular degrees).
Therefore at the set of probabilistic places only the wave part of electrons can be discovered in form of a longitudinal flow. This probabilistic statement is valid only for the time interval (T/2) in which the electron exists as a wave. The reason is that the longitudinal wave of the electron for part of the time (T/2) spills like a fluid into the surrounding space (S) .Thus during this time (T/2) the set of free electrons spill in the spaces and interact with each other.
Conclusion: The probabilistic set of all free electrons (in S) which probabilistic flows and spill during of half of period (T/2) may self-organizes, interacts and to make communications between them.
This spill encompasses all free (S) pulsating for (T/2) electrons and builds a pulsating environment of longitudinal accelerating vortices. It is very likely these longitudinal vortices self-organize in space (S) in depends on closeness of phases of pulsation in time (T/2).
It becomes already clear that the electron in half of period (T/2) of its pulsating it play role of particle, but in next half of the period (T/2) electron transforms to a wave. During the second half of period electrons as waves flows, outflows and spills out surrounding space with different parameters: amplitudes, frequencies and phases.
Conclusion: It exists a unique probabilistic field with distributed parameters of amplitudes, frequencies and phases.
Therefore, all free electrons in different chunks of the time will emit and spill their longitudinal Funnels. Their vortices, as fluid's waves will flow in different directions, with different amplitudes frequencies and with different phases. These waves form probabilistic field with distributed parameters Field with distributed parameters means that if in one point of space has longitudinal pulsating vortex with fixed parameters this pulsating vortex can do and can link the resonance system with a second participant at the very end of space. This happens based on their close parameters, despite the distances: The first participant is active accelerating vortex and it search and find the object for its orthogonal pair. The second participant of system is passive and is the orthogonal pulsating decelerating vortex at the very other end of space.
For Example: The accelerating vortices or accelerating Funnel emitted by one electron (Law1) can search, find and to pair itself in resonance system. Its partner (Axiom2) is an orthogonal decelerating vortices or decelerating Funnel that is sucked by the proton (Law2). But this proton governs its own electron by transverse decelerating vortex .The electron is located at very big distance in space and nevertheless it make connection with the proton.
Conclusion: Every resonance pair of mutual orthogonal vortices (Funnels) exchange longitudinal waves in form of Kinetic energy.
This means that pulsating pair of two (accelerating and decelerating) vortices exchange energy in very big distance between them. This energy is a Kinetic energy (E k). The kinetic energy is very likely to be carried by longitudinal velocity of wave of longitudinal vortex.
The active element in face of the accelerating Funnel (Law 1) of electron emits a central, the most accelerated longitudinal vortex distance.
Between accelerating and decelerating Funnels moves a longitudinal central vortex with velocity more than light speed (c). This accelerating central vortex is emitted from the accelerating active Funnel and is spread in first half of period to the passive decelerating part. This passive vortex (also an other vortex) returns back in second half of period to active Funnel. Therefore it is very likely the outgoing central vortex from accelerating Funnel and returning central vortex from decelerating Funnel (as waves) to form a standing wave .The standing wave forms many nodes and maxima during all distance.
Conclusion: The outgoing and returning central vortices form standing longitudinal wave with many nodes and peaks.
Such standing waves crossbreed all space in all directions in 3D. These 2 variable points form connections by standing waves with variable places, but necessarily with orthogonal parameters (amplitudes, frequencies and phases). Thus, these connections are not constant but probabilistic.
Conclusion: The connections by standing longitudinal waves are probabilistic in space(S) and in time (T).
Where the resistance is the least and the parameters are most suitable and orthogonal, the connection passes there. This means that the channel of standing waves is not a straight line but is some arbitrarily curved and zigzag line.
Conclusion: The channel of standing waves is not a line but it is arbitrarily curved or zigzag connection.
Therefore, these connections are not determined by location but are probabilistic, they are not on a straight line but on the line of (Law 6) with velocity equals to: v = ( v )N. least resistance, they are not stationary in time but are variable in time. These standing waves as accelerating longitudinal vortices
The accelerating longitudinal velocity (v N) of longitudinal vortex inserted in accelerating Funnel is more than light speed (c) of transverse waves of pulsating transverse vortices, where (vN) is velocity of central spiral, (v0) is velocity of periphery spiral, (N) is number of spirals in accelerating Funnel.
Conclusion: The central accelerating longitudinal velocity (v N) of longitudinal vortex inserted in center of accelerating Funnel is more than light speed (c).
The passive element in face of the decelerating Funnel (Law 2) of the proton sucks in the speediest central and the more periphery spirals .But the most peripheral spiral becomes most decelerated (Law 5). It opens in transversely directions the plane (in 2D) for rotating of accelerating transverse vortex that generates the proton (Law 2). The emitted wave and reflected wave form standing wave.
Conclusion: A standing longitudinal wave is formed by every resonance (mutual orthogonal) pair that communicates in big (Law6) have a speed not commensurate, but greater than the speed of light (c).
Conclusion: The standing longitudinal wave (as accelerating longitudinal vortex) has a speed more than light speed (c).
Note: May be these probabilistic connections by standing wave (as accelerating longitudinal vortices) have constant velocity (V) more than light speed (c). Thus it can define a new kind of time- space with V=const.
References
1. Landau, L. D. (Ed.). (2013). The classical theory of fields (Vol. 2). Elsevier.
2. Markova, V. (2003). The other axioms (Monograph, Book 1). Nautilus, Sofia.
3. Markova, V. (2005). The other axioms (Monograph, Book 2). Nautilus, Sofia.
4. Markova, V. (2019, September). Extended Field Theory, New Axioms, Laws and Consequences. In 2th International Conference on Quantum Mechanics & Nuclear Engineering, Paris, France.
5. Markova, V. (2017). Modeling of gravitational waves by creating a system of paired cross vortices. Some properties, conclusions and applications. IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP 9: 25-32.
6. Markova, V. (2017, July). New axiom for description of Gravity. In 5th International Conference on Physics, Athens, Greece (pp. 17-20).
7. Markova, V. (2018, July). About the new axioms and laws. In 5th International Conference on Theoretical and Applied Physics, Vienna, Austria.
8. Markova, V. (2019). Extended Field Theory, New Axioms, Laws and Consequences, 2nd International Conference on Quantum Mechanics & Nuclear Engineering, Paris, France.
9. Markova, V. (2019). Modeling of Two Different Space-times, Based on Knowledge of New Axioms and Laws, 2nd Global Summit on Physics, Paris, France.
10. Markova, V. Essence of Electric Charge of elementary particles according of New axioms and Laws, Adv Theo Comp Phy, 2020, ISSN: 2639-0108, Vol. 3, Iss. 4, 298-303.
11. Markova, V. (2021). System of electron-proton. Movement, rotation, pulsation and Gravity Forces. Adv Theo Comp Phy, 4(1), 14-22.
12. Markova, V. (2021). The Gravity Funnels, formed by the longitudinal vortices, according to the new Axioms and Laws, Adv. Theo. Comp. Phy, 4(1), 61-68.